National Petrochemical Industrial Company (NATPET)
Polypropylene or Polypropene (PP) is a unique versatile polymer in thermoplastic family. By virtue of its semi crystalline structure it has a very wide range of application. The material is ideal for both wet and dry process applications, offering a solid combination of mechanical strength, rigidity and dimensional stability. PP does not present stress-cracking problems and offers excellent electrical and chemical resistance at higher temperatures. Easily fabricated, thermoformed, vacuum formed, and welded.
Propylene (C3 H6) is polymerized to polypropylene in the presence of titanium-chloride or metalocene based catalyst. During polymerization, the CH3 groups can be incorporated in the macromolecule in spatially different ways. The resulting products have different properties and are classified as follows:
- Isotactic PP in the macromolecular chain the CH3 pendants are situated on the same side of the carbon chain.
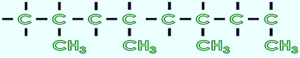
- The higher the isotactic content in the bulk polypropylene, the higher the degree of crystallinity achieved in the material. Most polypropylene we use is isotactic.
- Syndiotactic PP in this macromolecular chain CH3 pendants are alternately on one side of the chain and then on the other side as shown in figure 2. This structure can be produced with a metalocene based catalyst and/or Ziegler-Natta Catalyst with the association of external donor. This structure allows the production of a highly transparent and flexible PP.
- In syndiotactic PP in the macromolecular chain CH3 pendants are alternately on one side of the chain and then on the other side as shown in figure 2.
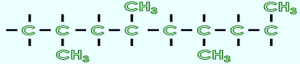
- This structure can be produced with a metalocene based catalyst and/or Ziegler-Natta Catalyst with the association of external donor.
- This structure allows the production of a highly transparent and flexible PP.
- In atactic PP in the macromolecular chain CH3 pendants are distributed randomly in their spatial position to the main chain as shown in figure 3.
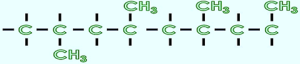
- An atactic PP structure does not allow the chains to pack themselves very tightly in order to form a three-dimensional (3-D) crystalline structure.
- The key properties of polypropylene as a material of choice are:
• High melting point makes it suitable for steam sterilization and hot filing.
• High chemical inertia makes it migration resistant and chemical resistant.
• High rigidity with Young’s modulus 2,000 (MPa) facilitates it to engineering plastic.
• High impact resistance even at low temperature.
• High environmental stress-cracking resistance
• Good Water barrier.
• Good transparency, especially with random copolymers.
• Recyclable – it can be re-melted and then reprocessed without loss of properties.Polypropylene is an economical material that offers a combination of outstanding physical, chemical, mechanical, thermal and electrical properties not found in any other thermoplastic. Compared to low or high density polyethylene, it has a lower impact strength, but superior working temperature and tensile strength.
Polypropylene can be processed by virtually all thermoplastic-processing method. Most typically PP Products are manufactured by: Injection Molding, Blow molding, Compression molding, Rotational molding, Injection blow molding, Extrusion Blow Molding, Injection stretch blow molding and General Purpose Extrusion. Expanded Polypropylene (EPP) may be molded in a specialized process.
Consumer
Battery Cases, Crates, Furniture, House ware, Luggage, Sports, Toys, Leisure
Rigid Packaging
Container, Thin walled molding (technical/food), Blow molding, Thermoforming, Medical, Caps & Closures, Corrugated board, Foam sheet.
Fibers and fabrics
Staple Fibers, Spun bond, Melt blown, Blown cast film (BCF), Cast film (CF), Raffia (cordage, netting, slit tape, luggage strapping), geotextile.
Flexible packaging
BOPP, Cast film, Blown film, Extrusion coating.
Automotive
Battery cases, Bumper, Exterior trims, Instrument panel, Interior trims, Under the hood.
Consumer Products:
Products classified in this sector are Housewares, Furniture, Luggage, Toys, Battery Cases and other “durable” items for home, garden or leisure use. Injection Molding dominates the conversion process used for these products. Market share of PP in this segment at present is 12%
Flexible Packaging:
PP is one of the leading materials used for film extrusion and has in recent years benefited versus cellophane, metals and paper on account of its superior puncture resistance, low sealing threshold and competitive price. PP Film is available either as Cast Film or bi-axially oriented PP (BOPP). The film market may be divided in to three main sectors.
• Food and Confectioneries
• Tobacco
• Clothing
The food and confectioneries sector is the largest of the film markets with usage ranging from confectioneries to crisps and biscuits. Tobacco products represent a significant market for PP (second largest after food and confectioneries).
Rigid Packaging:
Rigid packaging subdivides into a multitude of packaging applications from caps and closures to pallets and crates. Reusable and collapsible/stackable crates are a great application for PP, providing ease to transport (both full and empty) and allow simple, safe and efficient storage of products and are ideal for just-in-Time (JIT) storage solutions. As a consequence, supermarkets are beginning to revert to use and similar products are finding application in the automotive supply chain.
Caps and Closures manufactured from PP have benefited from growth in the PET bottle market, particularly for mineral water containment and that of edible oil.
PP is blow molded to produce bottles for the packaging of a range of products including condiments, detergent and toiletries markets.
PP thin-walled containers (e.g. yoghurt pots) are also common. PP competes with PS in this field by offering a cheaper material option (processing cost can, however, offset this benefit). PP is semi crystalline product and consequently has a narrower processing window than PS however improvement in additive package, e.g. nucleation during process makes the processing window wider for PP.
Automotive:
Polypropylene has a large application in automotive industry. Especially in battery cases PP is dominating for the last 25 years. With the need and trend of reducing the weight of cars, many components are changed to plastic parts from heavier materials like metals and wood. Now most of the plastic in cars is PP or PP compounds. PP film cushioning, film skins, and powder slush molding and even blow molded parts with integral PP textile covers are emerging.
Bumpers, cladding, and exterior/interior trim are also available manufactured from polypropylene. Polypropylene developed for such applications provides low coefficient of linear thermal expansion and specific gravity, high chemical resistance and good weather ability, process ability and impact/stiffness balance. Improvements with color-at-the-press and pre-colored PP have also reduced or eliminated the need for painting in some applications.
Polypropylene is quickly becoming a major material for automotive exterior parts as weight reduction has been an important factor in this industry.
Fibers and Fabrics:
A large volume of PP utilized in the market segment known as fibers and fabrics. PP fiber is utilized in a host of applications including raffia/slit-film, tape, strapping, bulk continuous filament, staple fibers, spun bond and continuous filament.
A major application of raffia is in carpet backings both primary and secondary types. The other major applications are twine, woven fabrics for feed and fertilizer sacks, jumbo bags, tarpaulins, mats, screen for erosion prevention, and geotextiles to stabilize soil beds. Continuous filament (CF) and bulked continuous filament (BCF) are mainly used as carpet face yarn and fabrics for upholstery.
Nonwoven fabrics account for more PP usage than any other single fiber application. Nonwoven fabrics are used in several areas like, liners in disposable diapers, feminine hygiene products, and medical applications. Monofilament are used in making ropes and twines, PP rope and twine are very strong and moisture resistant very suitable for marine applications.
Medical:
Polypropylene is the material of choice in medical application not only because of its light weight, low cost or both but also due to high chemical and bacterial resistance. For polypropylene it is possible to formulate PP compounding to enable them to undergo steam and radiation sterilization. The most notable such application is the disposable syringes. Polypropylene fulfills the essential need of a medical syringe extremely well. It can be precision-molded to yield the proper dimensions; it is clear enough to view the contents; it can be printed if necessary and can be irradiation-sterilized.
Medical vials, diagnostic devices, petri dishes, intravenous bottles, specimen bottles, food trays, pans, and amber-colored small containers that hold pills and capsules are also of PP products. ‘Sharp containers’ used to collect used syringes and other contaminated medical wastes are also the product of PP.
The other unique feature of PP that makes it ideal for medical use is its ability to be processed into nonwoven fabrics. The use of nonwoven in medical application is large and growing.
Industrial:
A material that has the attributes of tensile strength, a resistance to high temperatures and is highly resistant to corrosion, Polypropylene is a unique material for industrial use. Polypropylene is used in the manufacture of chemical tanks that are used for the mixing of liquid materials that may have slight corrosive properties as part of their compounds. In industrial sector polypropylene is used to manufacture a range of sheet, pipe, compounding and Returnable Transport Packaging (RTP). With the exception of RTP where Injection Molding is used, extrusion dominates the conversion process used for these products. Some PP is utilized by the construction sector, most notable domestic drainage pipes.
Conclusion:
Polypropylene has virtually endless uses, and its development has not slowed since its discovery. Whether used for industrial molds, rugged currency, car parts, or storage containers, it is one of a handful of materials the world is literally built around.
